Promoter
BIMSA-Ajuntament de Barcelona
Authors
Territori 24 Arquitectura i urbanisme
Location
Barcelona
Project / construction year
2012 – 2014
Surface
1.652 m²
Budget
2.176.771,18€
(vat included)

Energetic and socially
sustainable construction
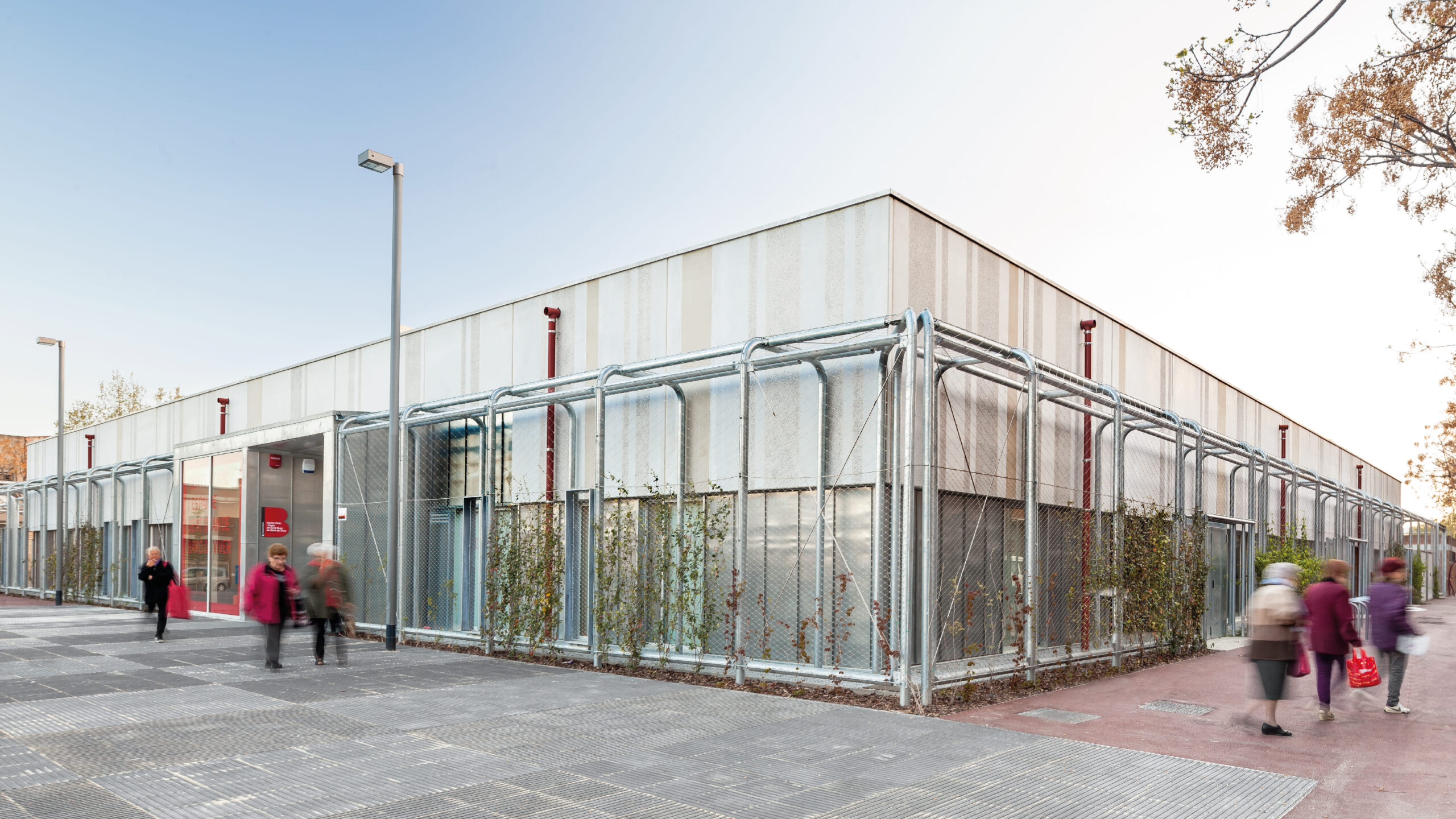
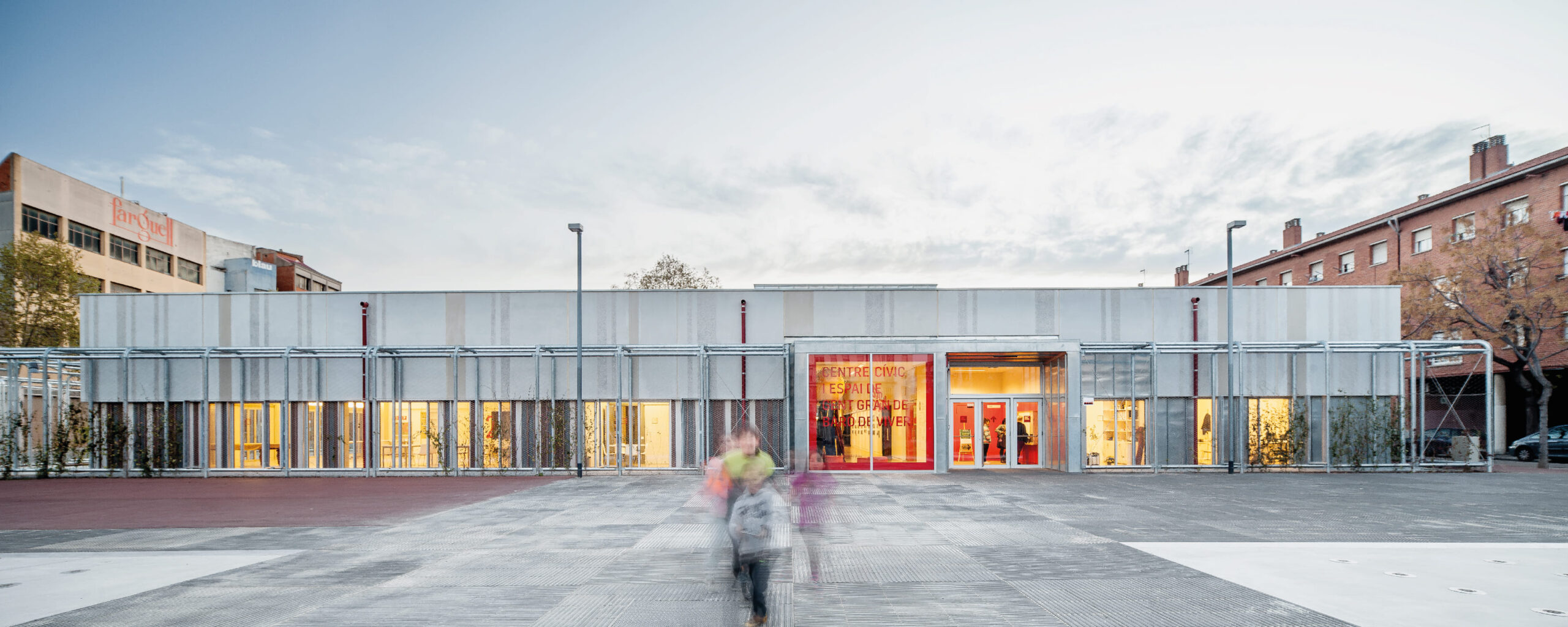
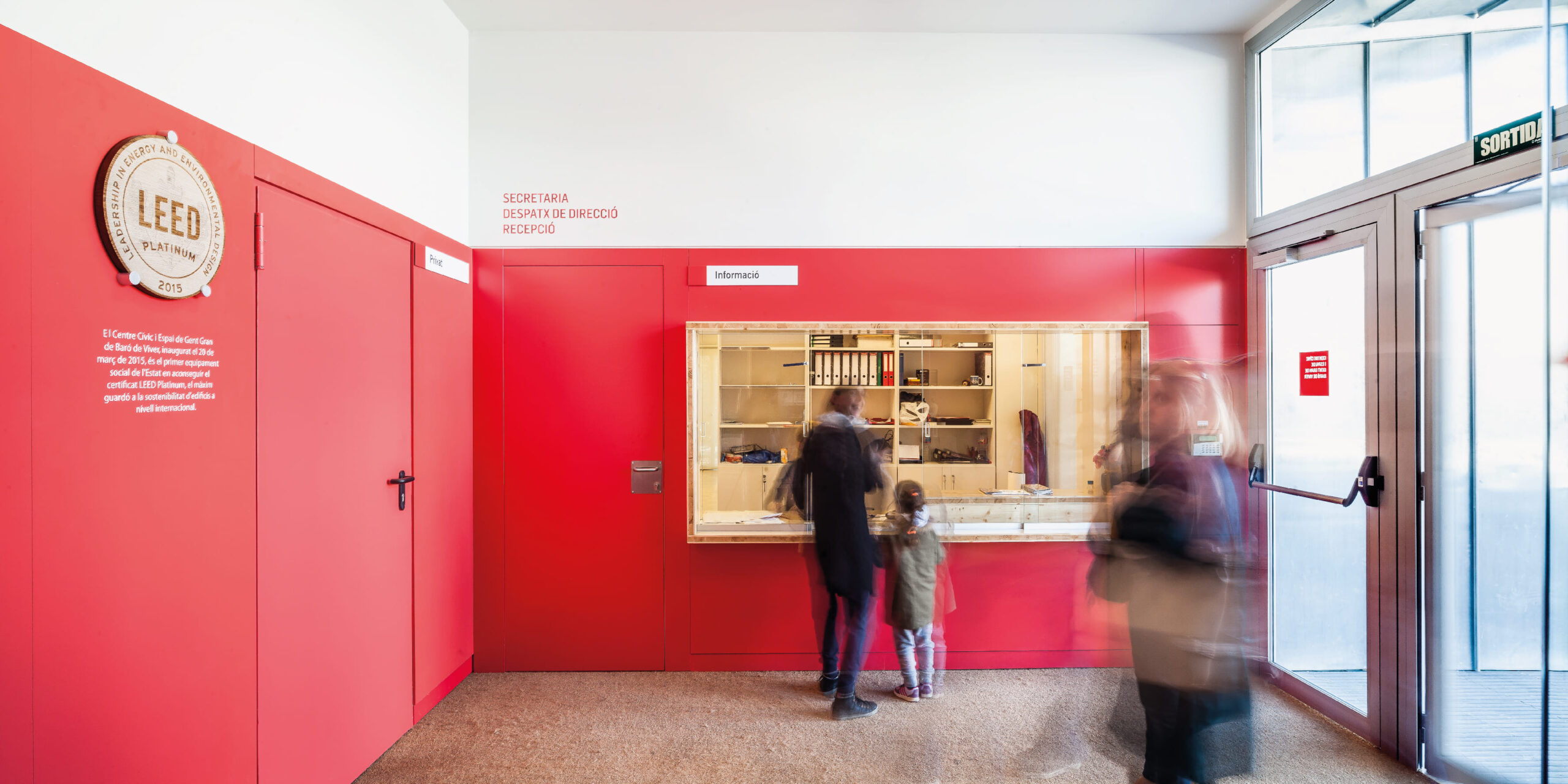
The new Baró de Viver Civic Center and Elderly Space is the first social facility with LEED Platinum certification for New Construction in the State.
Beyond achieving an A energy certificate, it attains the highest recognition for sustainability by embracing a holistic approach to the project, integrating architecture and energy efficiency solutions. It combines high-quality spaces for users with notable energy efficiency, avoiding major technological ostentation, all within a budget 34% lower than a standard facility in the city of Barcelona.
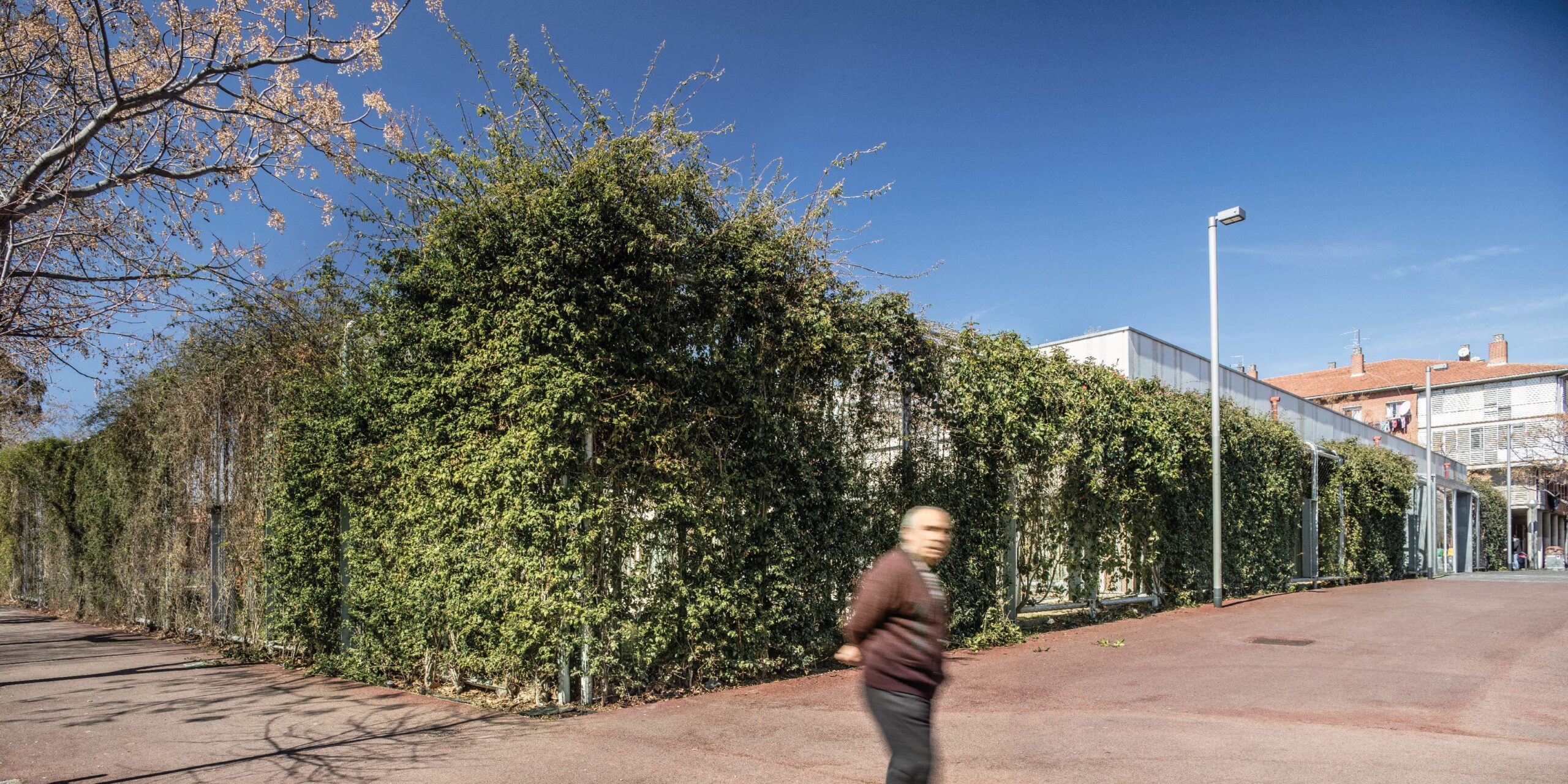
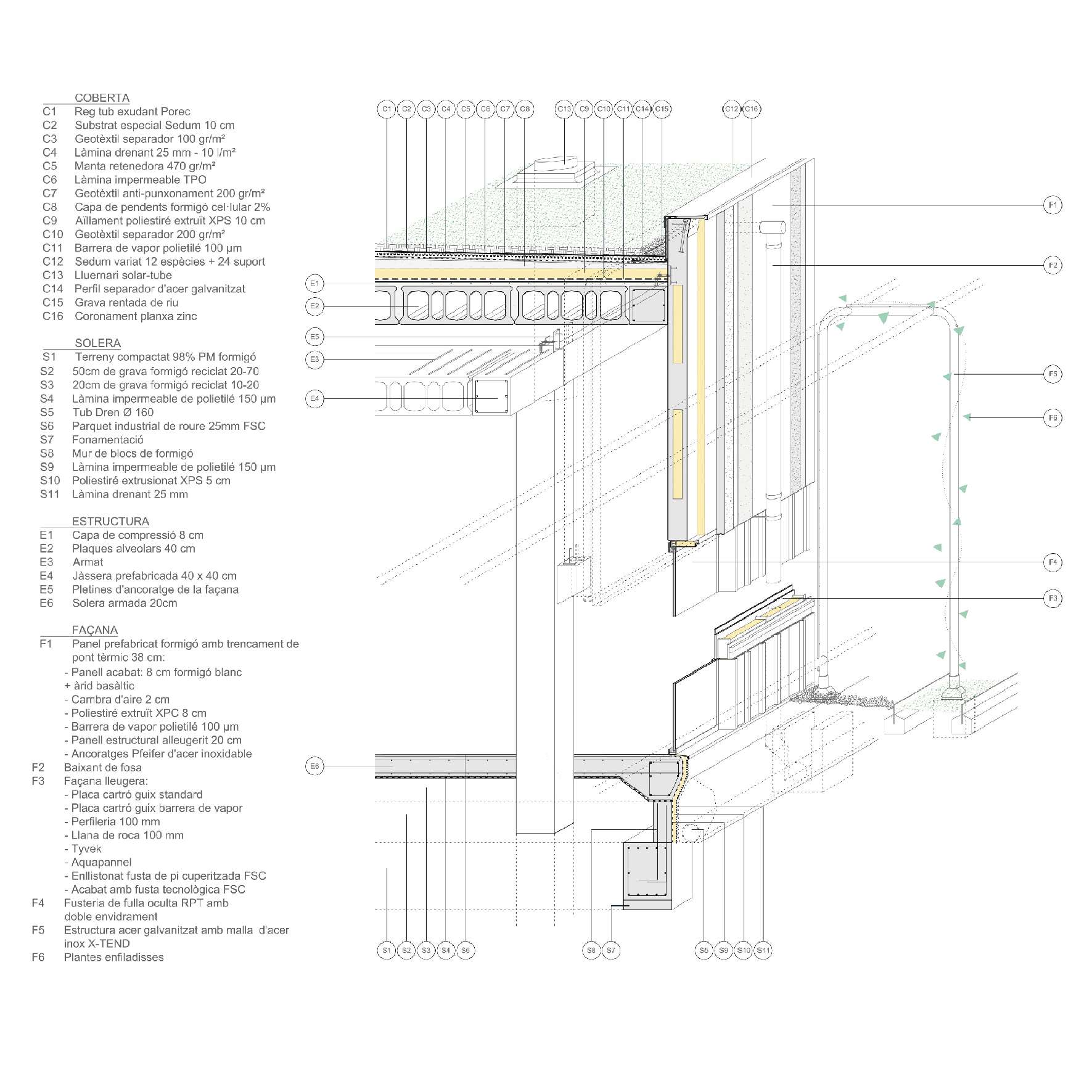
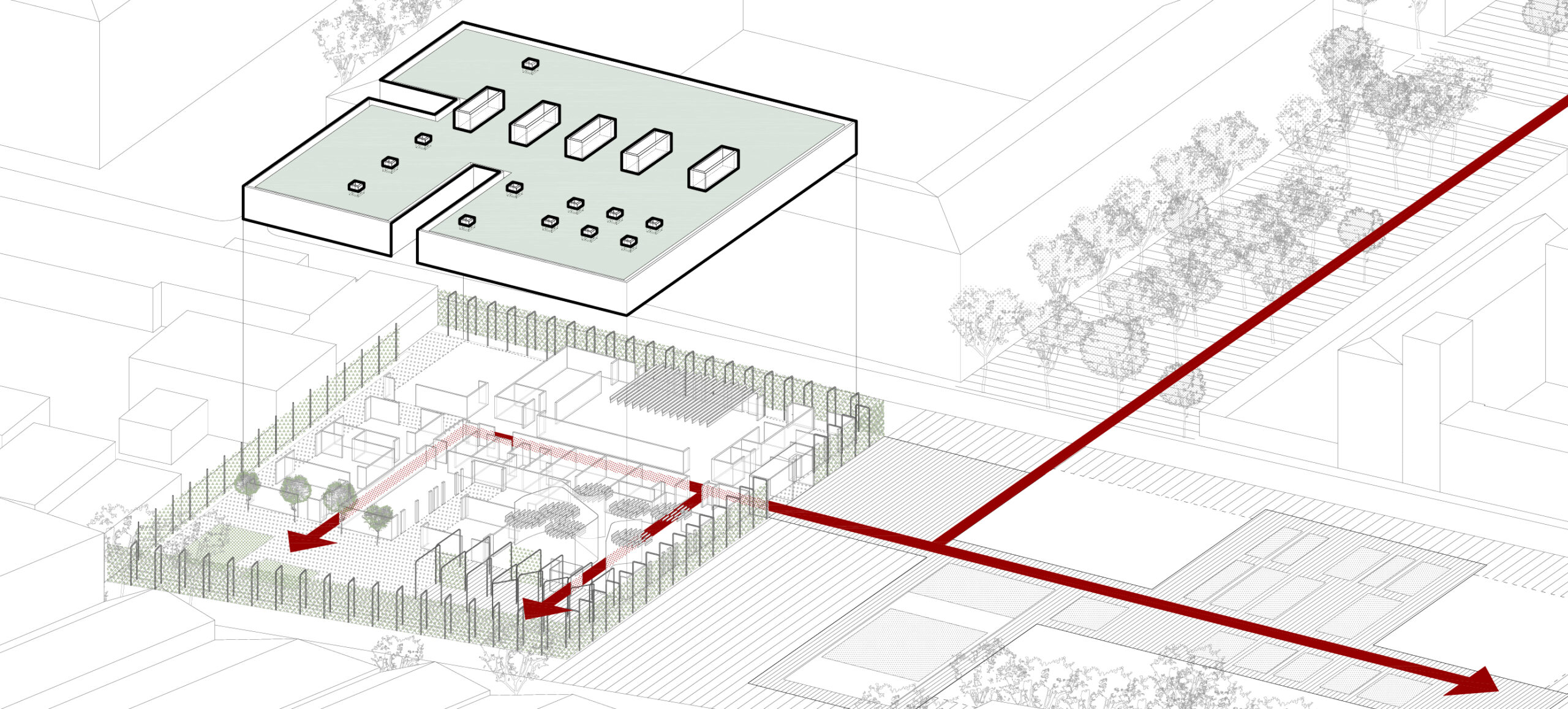
Energy saving and sustainability.
A low-tech building is designed, based on a prefabricated system, which achieves high environmental efficiency based on strategies to reduce energy demand and use prefabricated economic structural and construction systems.
By applying these criteria, we manage to construct a highly sustainable building without increasing the budget.
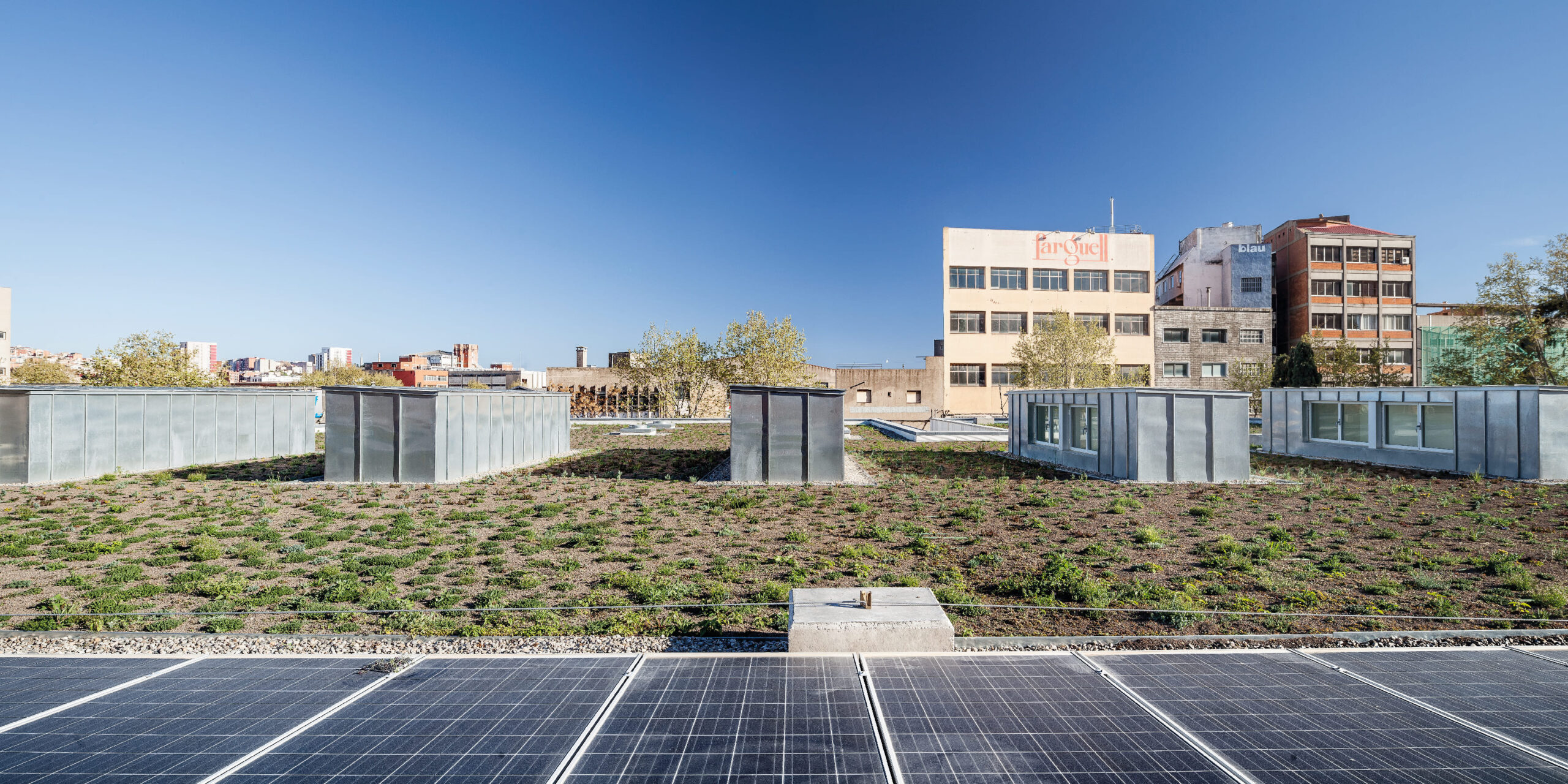
Using an advanced energy modelling, we dimension the elements and the system, to re-invest in renewable energy, the reuse of rainwater, green roof and a solar tube system to reduce electricity consumption.
The building consumes 48% less than a standard building and generates a significant portion of the consumed energy on its own.



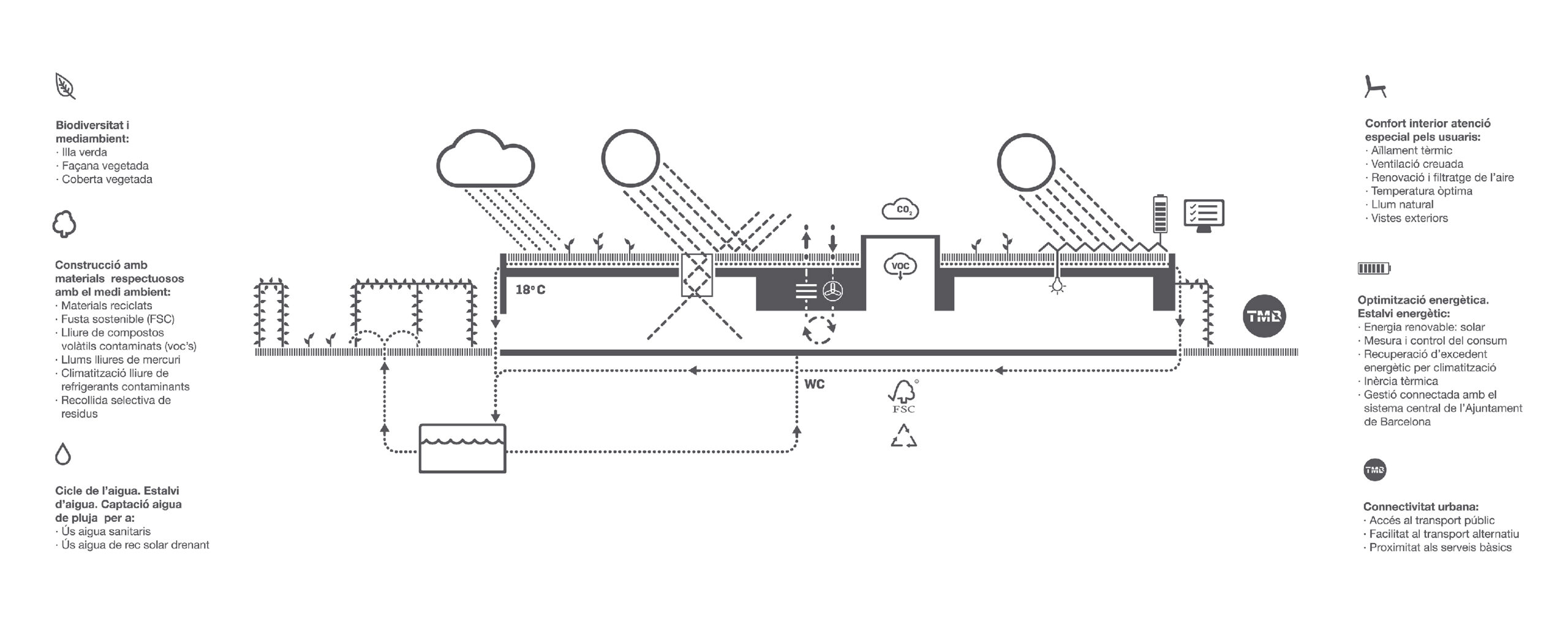
Sustainability
The building consumes 48% less than a standard building in the year of its construction. It is designed so that cooling is not needed in the summer, relying on thermal inertia and ventilation for climate comfort.
100% of the water for irrigation of the building and sanitary facilities comes from rainwater.
It is a building free of contaminants such as VOC and mercury, ensuring environmental quality.
Completely prefabricated and constructed in a dry manner, it reduces the impact and emissions of its entire life cycle by 41%.




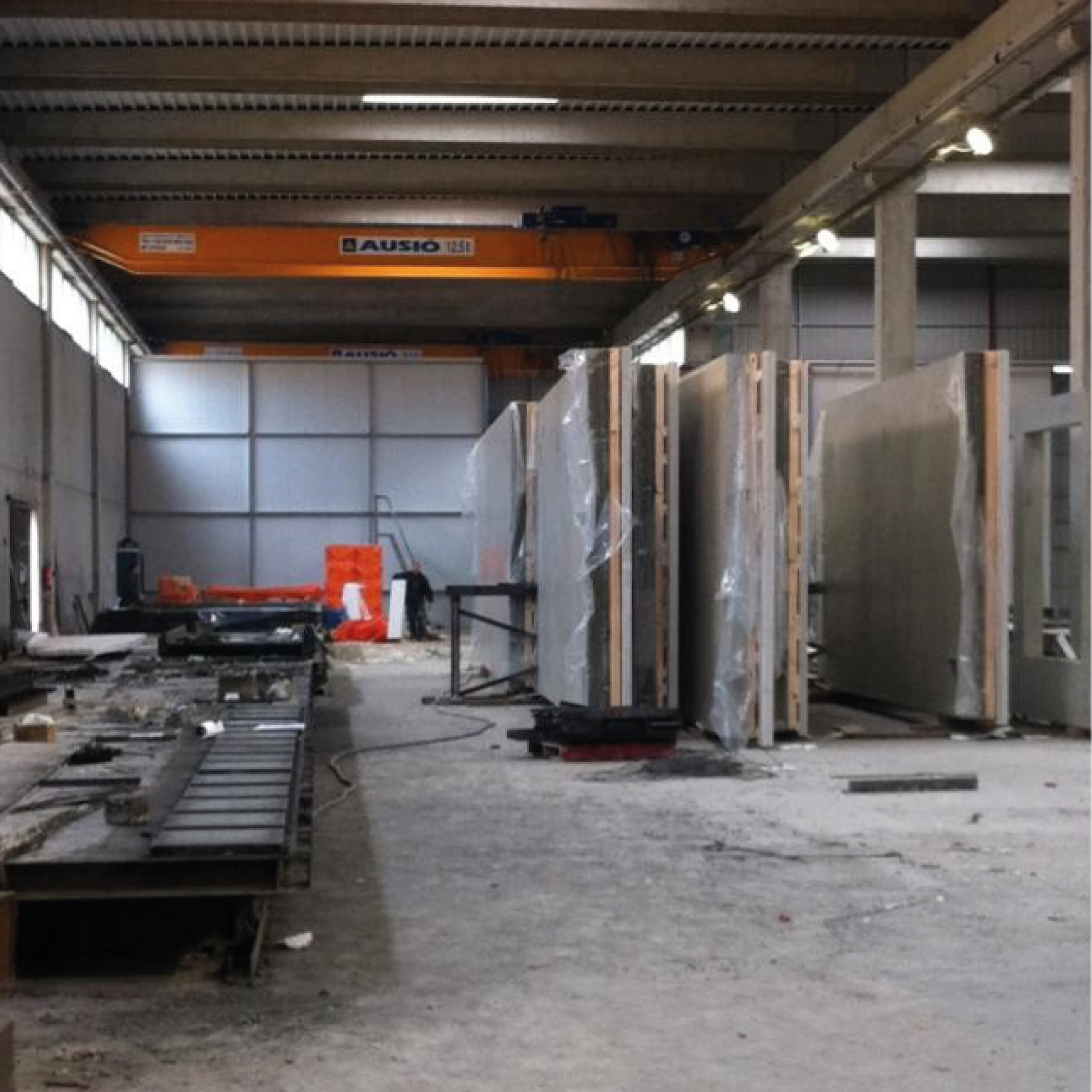
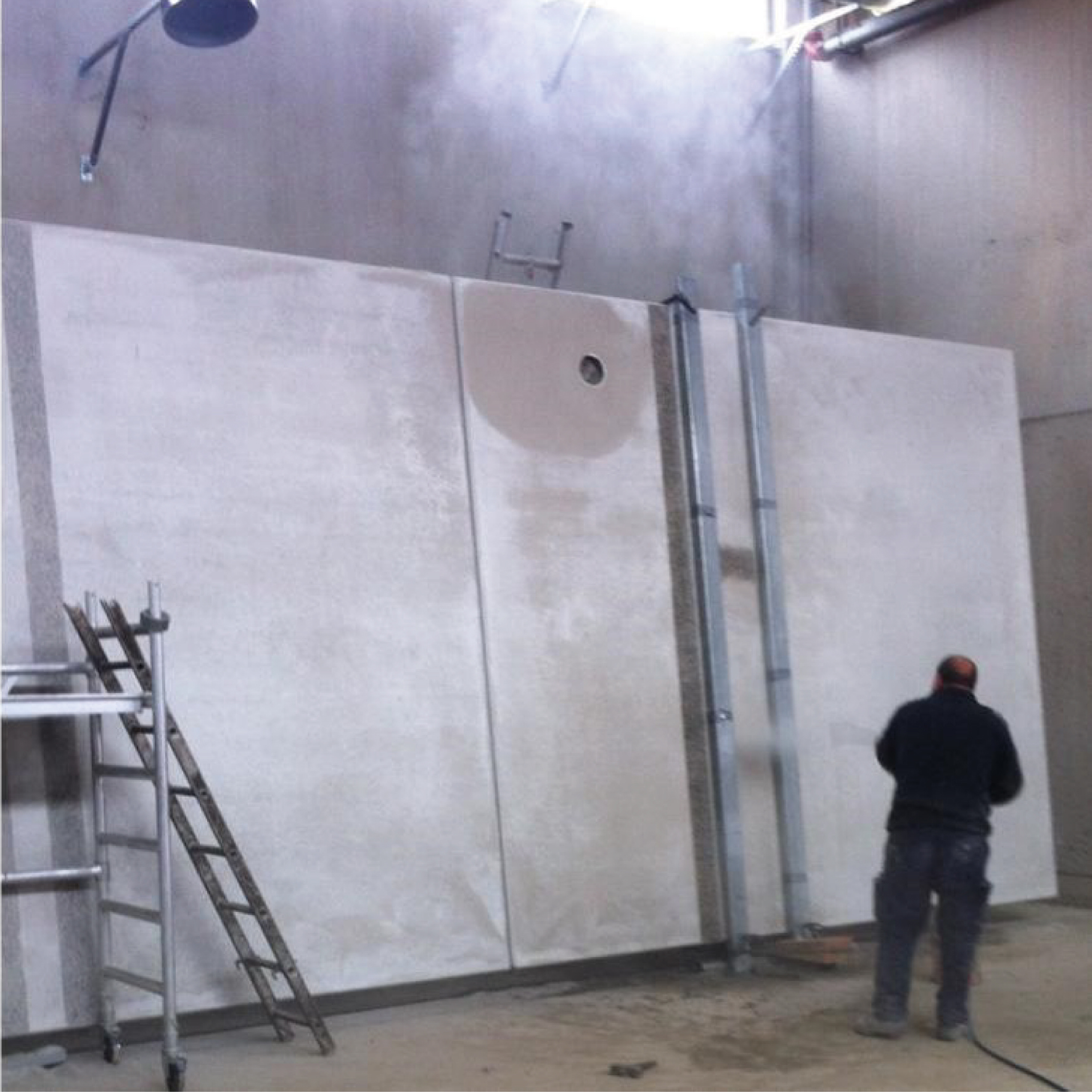
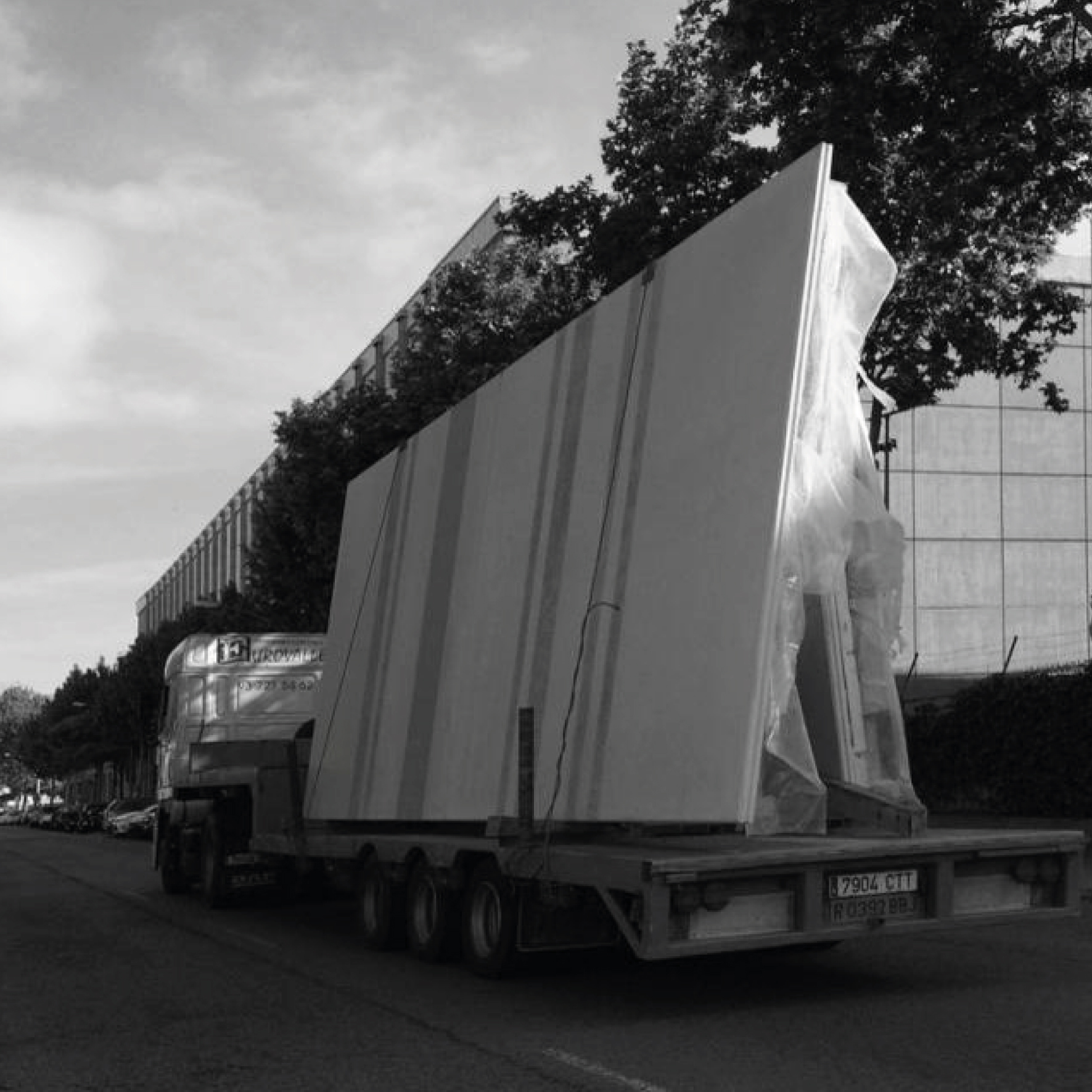
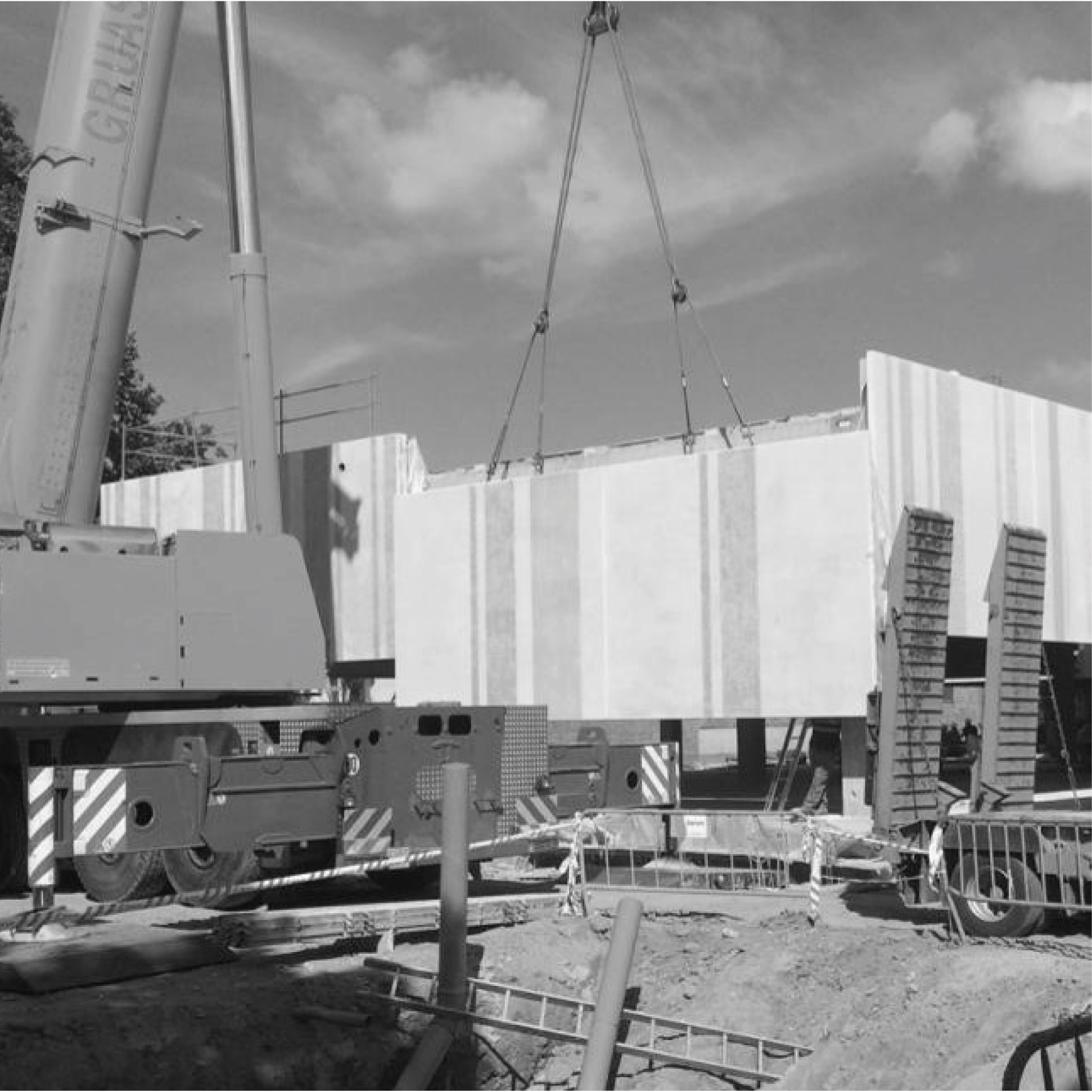
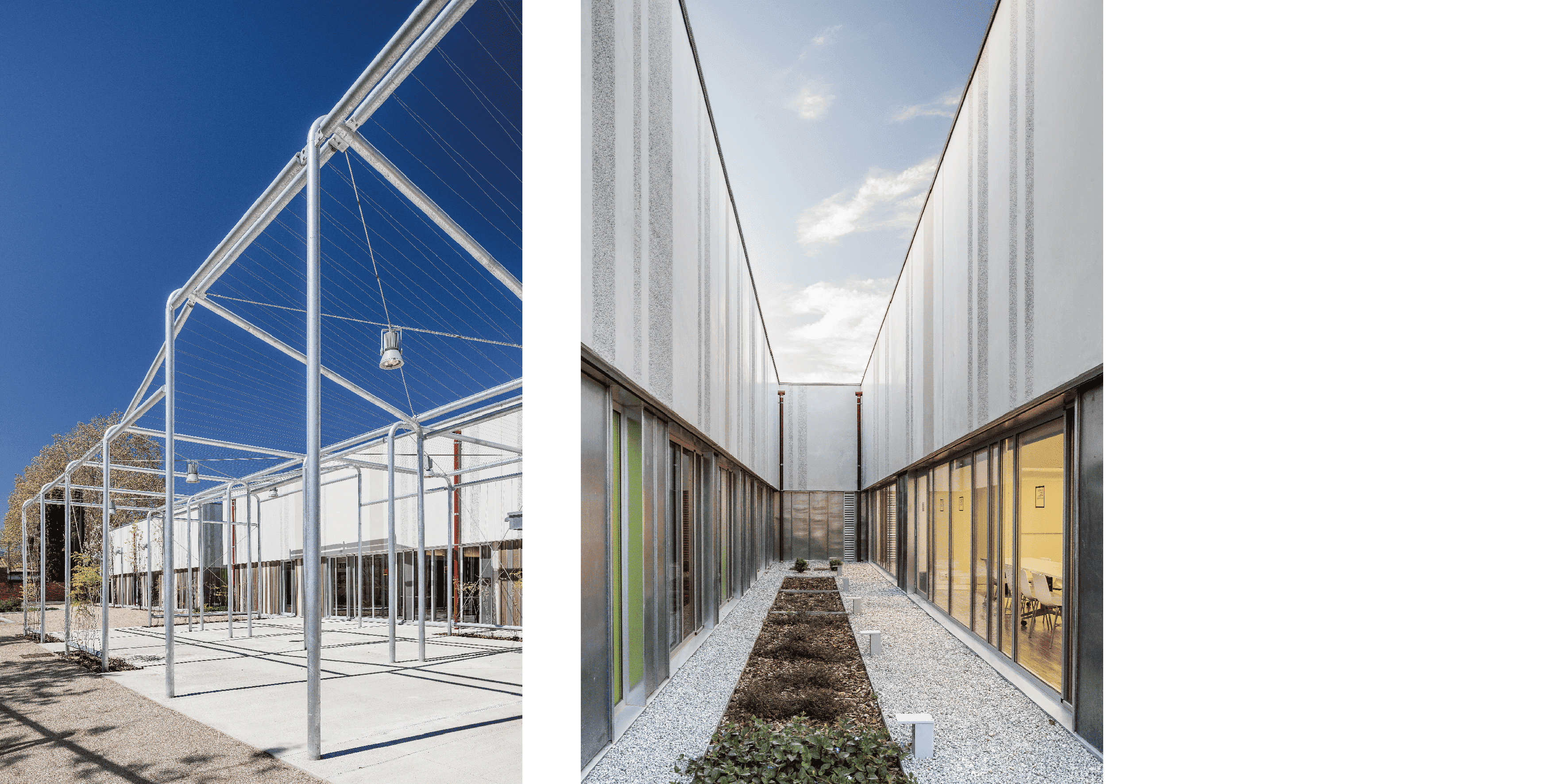
Pre-industrialized systems
The use of various pre-industrialized systems allowed optimizing the execution process.
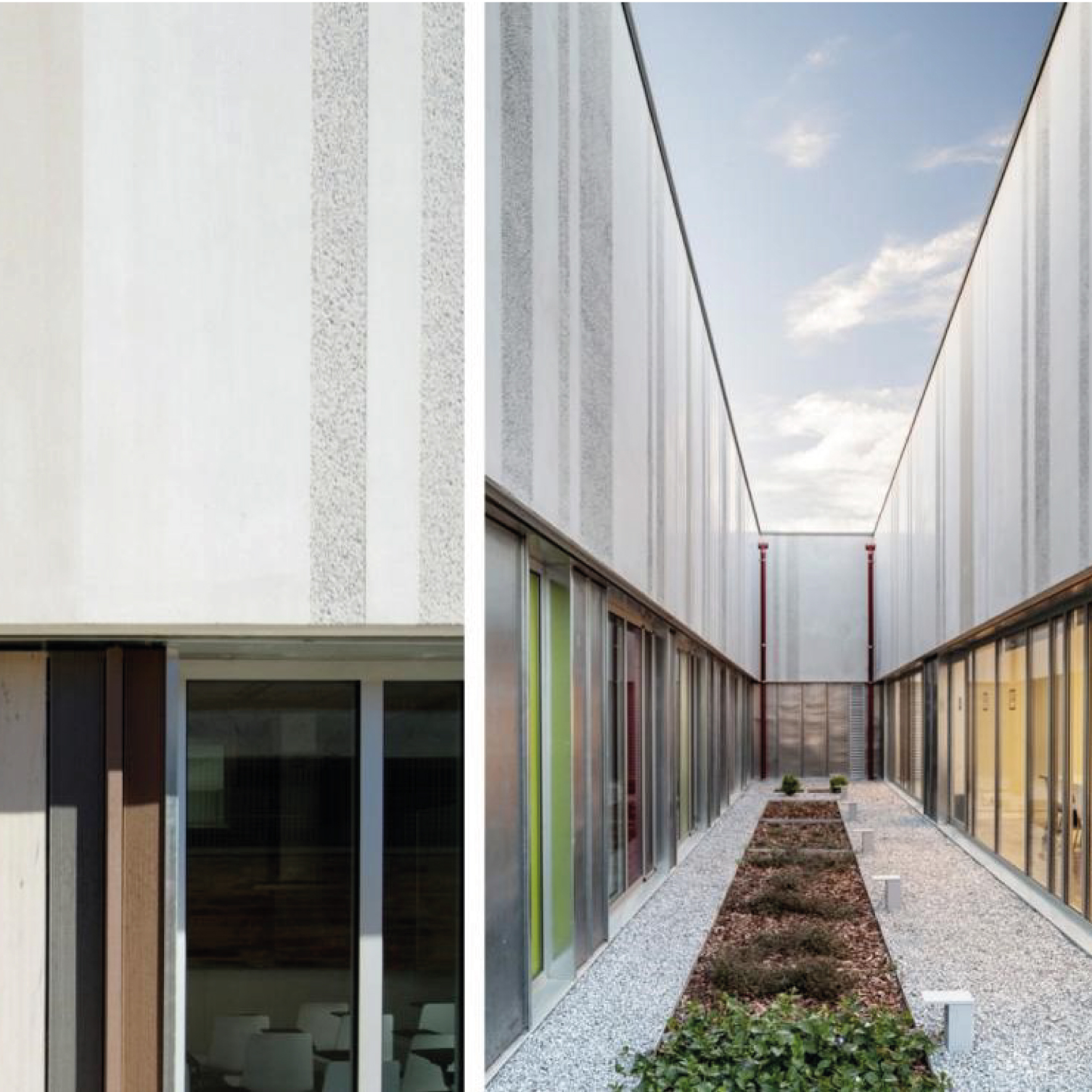
The facade is divided into two horizontal sections. The upper section consists of precast architectural concrete panels with thermal bridging, incorporating finish, air chamber, insulation, and support structure.
The lower section incorporates the openings for each room based on its orientation and energy load.
The windows are combined with an exterior cladding made of technological wood.